Imagine a world where machines can think, learn, and adapt, this is no longer science fiction. From self-driving cars to personalized Netflix recommendations, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) transform how we live and work. But what exactly sets these two revolutionary technologies apart? Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are two of the most significant technological advancements shaping our world today.
This guide will walk you through their definitions, how they work , their key differences, and their real-world applications. By the end, you’ll clearly understand their impact on our lives and their immense potential for the future. Let’s dive deeper to understand what makes them unique and how they power the modern era.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence refers to machines designed to simulate human intelligence, enabling them to think, reason, and solve problems. AI can analyze information, make decisions, and improve itself over time. This concept was first introduced in the 1950s, but it has rapidly evolved thanks to advancements in computing power and data availability.
Core Objectives of AI:
- Mimicking Human Reasoning: AI systems replicate human-like decision-making processes. Example: Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa respond to questions and perform tasks as if they were human.
- Solving Complex Problems: AI tackles tasks like playing chess or mapping the human genome—challenges often beyond human capabilities.
- Learning and Adapting: Modern AI systems, like self-driving cars, analyze data to learn and improve their performance.
Applications of AI:
- Healthcare: AI diagnostic tools, like IBM Watson Health, help identify diseases with precision, such as detecting early-stage cancer.
- Finance: AI detects fraudulent transactions in real time, minimizing financial risks.
- Transportation: AI powers autonomous vehicles like Tesla, interpreting road signs and avoiding collisions to ensure safety.
- Customer Service: Chatbots powered by AI handle thousands of customer queries efficiently.
How It Feels Like in Everyday Life: Have you ever asked Alexa to play your favorite song or noticed how your phone’s camera can identify and focus on your face? That’s AI in action, making life more seamless and interactive. But do u know from where AI gets its information?
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on enabling machines to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. Instead of following pre-written rules, ML systems analyze data to identify patterns and make predictions.
Core Objectives of ML:
- Pattern Recognition: ML systems uncover insights from vast datasets. Example: Google Photos identifies faces in your images by recognizing unique features.
- Predictive Analytics: ML models forecast weather patterns, stock market trends, or even consumer behavior.
- Continuous Improvement: ML algorithms, like Spotify’s recommendation engine, refine their output based on user interactions.
Applications of ML:
- Retail: Amazon’s product recommendations are powered by ML algorithms analyzing your shopping habits. For instance, recommending a laptop sleeve after you purchase a laptop.
- Cybersecurity: ML systems detect unusual login patterns and block potential cyber threats, securing sensitive data.
- Social Media: Instagram’s explore page suggests posts tailored to your interests, using ML algorithms to analyze your engagement patterns.
How It Feels Like in Everyday Life: Ever notice how Netflix seems to know exactly what you want to watch next? That’s ML at work—analyzing your preferences and making predictions to keep you hooked.
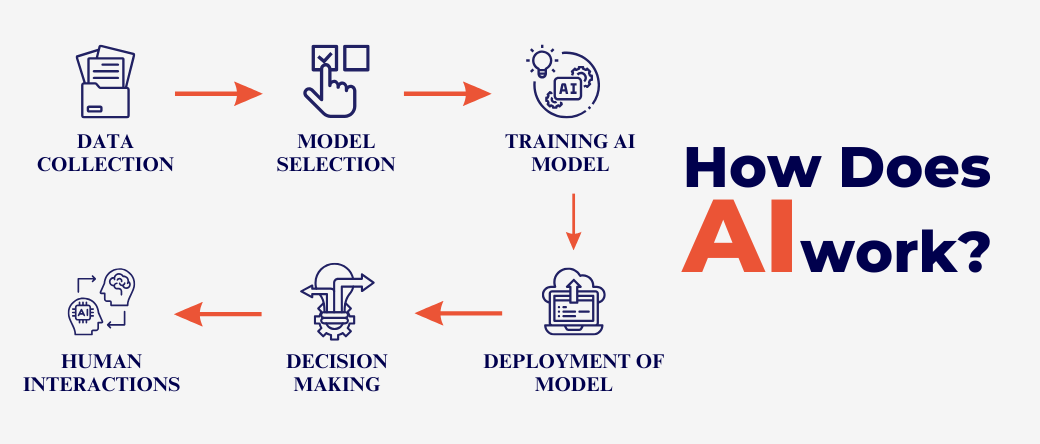
How Does AI Work?
AI operates through algorithms, vast datasets, and computational power. Here’s how:
- Data Collection: AI gathers and organizes massive amounts of data. Example: Chatbots analyze conversations to better understand user needs and provide relevant responses.
- Algorithm Development: Developers create algorithms that simulate human decision-making processes. Example: Neural networks replicate how our brains process visual information, allowing AI to recognize images.
- Training and Learning: AI systems learn by processing data and refining their decision-making capabilities. Example: Google Translate improves its language translations as it processes more multilingual data.
- Execution: Once trained, AI performs tasks like diagnosing diseases, generating creative art, or filtering spam emails.
Key Techniques in AI:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables AI to understand and generate human language. Example: Customer service chatbots that provide instant responses.
- Computer Vision: Allows AI to interpret images. Example: Facial recognition in smartphones that unlock your phone instantly.
- Reinforcement Learning: AI learns through trial and error. Example: Robots in factories learning to optimize their movements to speed up production lines.
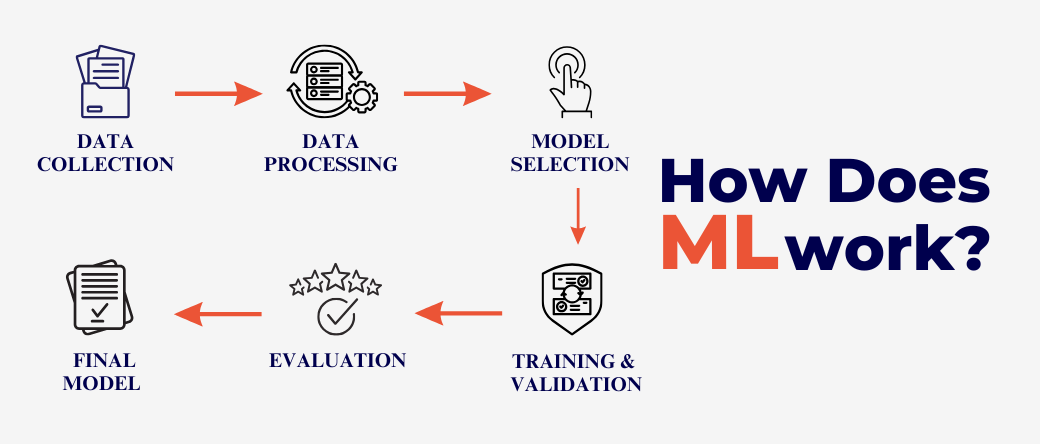
How Does ML Work?
ML systems learn from data using these key steps:
- Data Input: Raw data is collected and cleaned for analysis. Example: Netflix gathers your watch history, ratings, and pauses to improve recommendations.
- Feature Selection: Important attributes are identified to enhance predictions. Example: In healthcare, an ML model may focus on patient age, symptoms, and medical history to predict illnesses.
- Model Training: Algorithms analyze data to detect patterns. Example: Fraud detection systems learn the typical behaviors of customers to flag anomalies.
- Testing and Validation: Models are tested on separate datasets to ensure accuracy before deployment.
- Deployment: Once optimized, the ML system is implemented for real-world applications. Example: Predicting delivery times in logistics with near-perfect accuracy.
Types of Machine Learning:
- Supervised Learning: Models learn from labeled data. Example: Email spam filters that identify junk mail.
- Unsupervised Learning: Systems find patterns in unlabeled data. Example: Grouping customers into segments for targeted marketing.
- Reinforcement Learning: Models learn through trial and error. Example: Self-driving cars improving navigation routes based on traffic patterns.
How Are AI and ML Related?
Does ML Encompass AI? While Machine Learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence, it does not encompass AI as a whole. AI includes various other technologies like robotics, expert systems, and natural language processing that go beyond ML’s focus on pattern recognition and learning from data. In short, ML is just one piece of the broader AI puzzle.
AI is the overarching concept of creating machines capable of intelligent behavior, while ML is a specialized branch of AI focused on learning from data. Think of AI as the parent and ML as its child.
Other Branches of AI:
- Expert Systems: Rule-based systems for decision-making. Example: Diagnosis software for medical professionals that suggests treatments based on symptoms.
- Robotics: Machines that perform physical tasks. Example: Assembly-line robots in factories that manufacture cars.
- Deep Learning: A subset of ML using neural networks. Example: AI systems that recognize and caption images, like those on social media platforms.
Common Misconceptions
AI vs. Sci-Fi
Movies and television often depict AI as sentient robots with emotions and consciousness, leading to the misconception that all AI systems are advanced humanoid entities. In reality, most AI systems are designed for specific tasks, such as recommending products or detecting fraudulent transactions. For example, while AlphaZero can master complex games like chess, it cannot hold a conversation or perform unrelated tasks. Understanding AI as task-specific helps demystify its capabilities.
ML Is Always Accurate
Machine Learning models are powerful but not infallible. Predictive systems can make errors, particularly if trained on poor-quality or incomplete data. For instance, an ML model predicting weather patterns may fail during extreme or rare climate events. Continuous monitoring, retraining, and improving data quality are essential to maintain accuracy. It’s important to approach ML outputs as informed estimates rather than absolute truths.
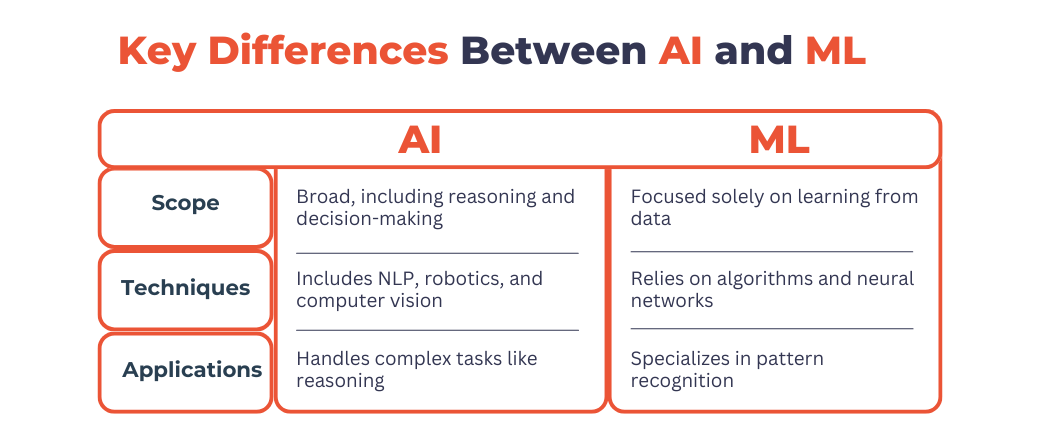
Key Differences Between AI and ML
Applications of AI and ML (With Examples)
Artificial Intelligence:
- Virtual Assistants: Siri and Alexa process voice commands and provide answers, simplifying daily tasks.
- Smart Cities: AI traffic systems reduce congestion in cities like Singapore by analyzing traffic flow in real time.
- Gaming: Chess bots like AlphaZero develop new strategies during matches, challenging even world-class players.
Machine Learning:
- Healthcare: ML predicts disease progression, like detecting early-stage cancer in patients.
- Finance: Detects unusual credit card transactions to prevent fraud before it happens.
- Education: Platforms like Duolingo recommend lessons based on your learning progress, personalizing the experience.
Ethical Considerations in AI and ML
Data Privacy and Consent
AI and ML systems often require vast amounts of data to function effectively. This data can include sensitive information such as personal health records, financial details, or even behavioral patterns. For example, fitness trackers collect user health data to offer insights, but users may not fully understand how their data is stored, shared, or used. It is crucial for companies to ensure transparency in data collection and obtain explicit consent from users. Privacy frameworks like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU emphasize the importance of securing user data and giving individuals control over how their data is handled.
Bias and Fairness
Bias in AI and ML systems arises when the training data reflects societal biases or lacks diversity. For instance, a facial recognition system trained primarily on light-skinned individuals may perform poorly on darker-skinned individuals, leading to unfair outcomes. Bias can also emerge in hiring algorithms that inadvertently favor certain demographics. Addressing this requires diversifying training datasets, regularly auditing models, and implementing fairness guidelines to minimize discriminatory outcomes.
Regulatory Landscape
Governments and organizations are working to establish regulations that ensure the ethical use of AI and ML. The GDPR sets strict guidelines for data privacy, while countries like the US and China are drafting AI-specific legislation. Additionally, initiatives like the Ethical AI Principles by UNESCO aim to create a global framework for responsible AI development. Adhering to these regulations not only fosters trust but also protects companies from legal liabilities.
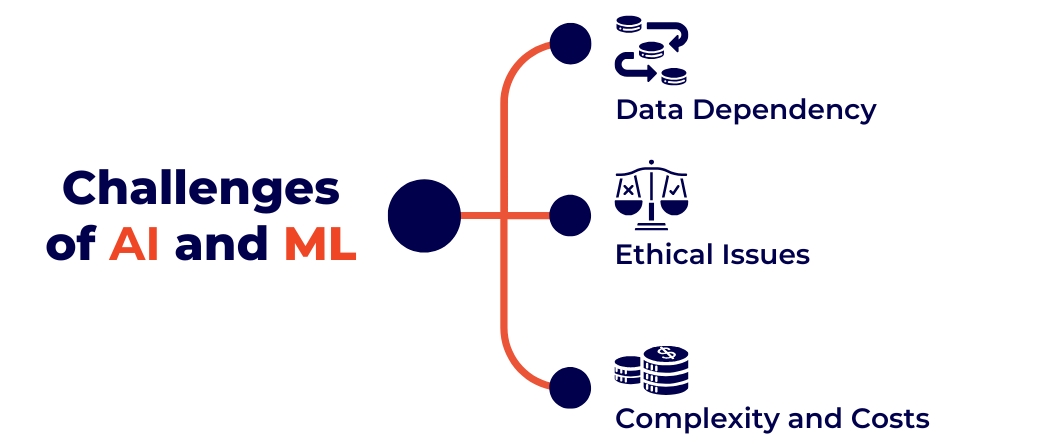
Challenges of AI and ML
- Data Dependency: Systems require high-quality, unbiased data to function. Example: AI hiring tools risk making biased decisions if trained on flawed datasets.
- Ethical Issues: Privacy concerns arise when sensitive data is collected. Example: Facial recognition in public spaces can lead to misuse.
- Complexity and Costs: Building AI systems can be resource-intensive. Example: Developing autonomous vehicles involves extensive testing and specialized hardware.
Integration with Other Emerging Technologies
IoT (Internet of Things)
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects physical devices to the internet, generating vast amounts of data. AI and ML play a critical role in analyzing this data to make smart decisions. For example, smart home systems powered by IoT and AI can learn user habits, automatically adjusting lighting, heating, and appliances to optimize comfort and energy efficiency. In agriculture, IoT sensors collect soil and weather data, while AI processes this information to recommend the best planting schedules and irrigation methods.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology complements AI by providing secure, transparent data storage. For example, in healthcare, blockchain can ensure that patient data used to train AI models remains tamper-proof and confidential. Additionally, AI algorithms can analyze blockchain transaction patterns to detect fraud in cryptocurrency markets. This combination of technologies enhances trust and accountability in data-driven systems.
AR/VR
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are being supercharged by AI to create immersive and interactive experiences. AI-powered AR apps can overlay real-time information, such as translating foreign text when viewed through a smartphone camera. Similarly, VR environments use AI to simulate realistic scenarios, making them ideal for training purposes in industries like aviation and medicine. For instance, pilots can practice emergency protocols in AI-driven VR simulations.
Future of AI and ML
The future holds limitless possibilities for these technologies:
- AI-Augmented Creativity: Tools like DALL-E generate art based on text prompts, enabling creative projects.
- Climate Change Solutions: ML models predict deforestation trends, aiding conservation efforts and environmental strategies.
- Healthcare Innovations: AI detects diseases like Alzheimer’s early through advanced imaging and analysis.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are reshaping our world in profound ways. From personalized experiences to groundbreaking innovations, understanding their differences and applications helps us embrace their potential. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or a business leader, learning about AI and ML equips you to navigate a future driven by intelligent systems.
Unlock the Power of AI & ML – Transform Your Future Today!
FAQs:
1. What is the difference between AI and ML?
AI is the broader concept of creating intelligent machines, while ML is a specific subset focused on enabling machines to learn from data without explicit programming.
2. How does Machine Learning work?
ML systems learn from data through a process that involves:
- Data collection and preparation: Gathering and cleaning data.
- Feature selection: Identifying the most important attributes for analysis.
- Model training: Algorithms analyze data to identify patterns and make predictions.
- Testing and validation: Evaluating the model’s accuracy.
- Deployment: Implementing the model for real-world use.
3. What are some real-world applications of AI?
AI powers many aspects of our daily lives, including:
- Virtual assistants: Siri, Alexa (improve your daily routine by asking them questions)
- Self-driving cars: Navigate roads safely and efficiently (book a test drive in a self-driving car today!)
- Healthcare: Diagnose diseases, personalize treatment plans (schedule a consultation with an AI-powered healthcare provider)
4. What are some real-world applications of ML?
ML is used in various fields, such as:
- E-commerce: Personalized product recommendations (browse our AI-powered recommendations and find your next favorite product)
- Finance: Fraud detection, algorithmic trading (invest smarter with our AI-powered investment platform)
- Social media: Tailored content suggestions (discover new content that interests you on our platform)
5. What are the challenges of AI and ML?
Some key challenges include:
- Data bias: AI systems can reflect biases present in the data they are trained on.
- Ethical concerns: Issues related to privacy, job displacement, and the potential for misuse.
- Complexity and cost: Developing and maintaining AI/ML systems can be expensive and resource-intensive.
6. What is the future of AI and ML?
The future holds exciting possibilities for AI and ML, including:
- AI-powered creativity: Tools that generate art, music, and literature.
- Solving global challenges: Addressing climate change, improving healthcare, and combating poverty.
- Enhanced human capabilities: AI assistants that augment our cognitive abilities.






